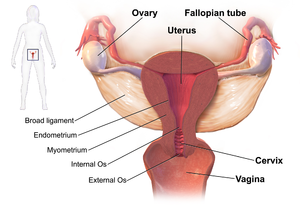
Fallopian tube obstruction is a major cause of female infertility. Blocked fallopian tubes are unable to let the ovum and the sperm converge, thus making fertilization impossible. Fallopian Tubes are also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, and salpinges (singular salpinx).
Fallopian tubes are a crucial part of the reproductive system. The proper functioning of the fallopian tube is essential for a successful pregnancy. These tubes aid in the transportation of the mature egg from ovary towards the uterus. If sperms are present, then the fertilization of sperm and egg takes place in the fallopian tube itself. Hence you know how fallopian tubes function and act as essential components for a successful pregnancy. At times, fallopian tubes have certain types of blockage that hamper the occurrence of normal pregnancy in a smooth way. Due to such blockages, it gets difficult for a woman to conceive as the fertilized egg and sperm (zygote) is not transported into the uterus for implantation.
What are the causes of Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
1. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease is one of the most commonly detected causes of the fallopian tube blockage. In this disease, there is an inflammatory effect, which causes the reproductive organs including the fallopian tube to get swelled up. This inflammation stops a woman from conceiving; it can also result in miscarriages or even an ectopic pregnancy where the embryo is implanted inside the fallopian tube. In an ectopic pregnancy, the embryo gets stuck inside the tube instead of travelling towards the uterus due to the scarring of fallopian tubes.
2. Fibroids
Fibroids are abnormal growths that develop in or on a woman’s uterus. Sometimes these tumors become quite large and cause severe abdominal pain and heavy periods. In other cases, they cause no signs or symptoms at all. The growths are typically benign, or noncancerous. The cause of fibroids is unknown.
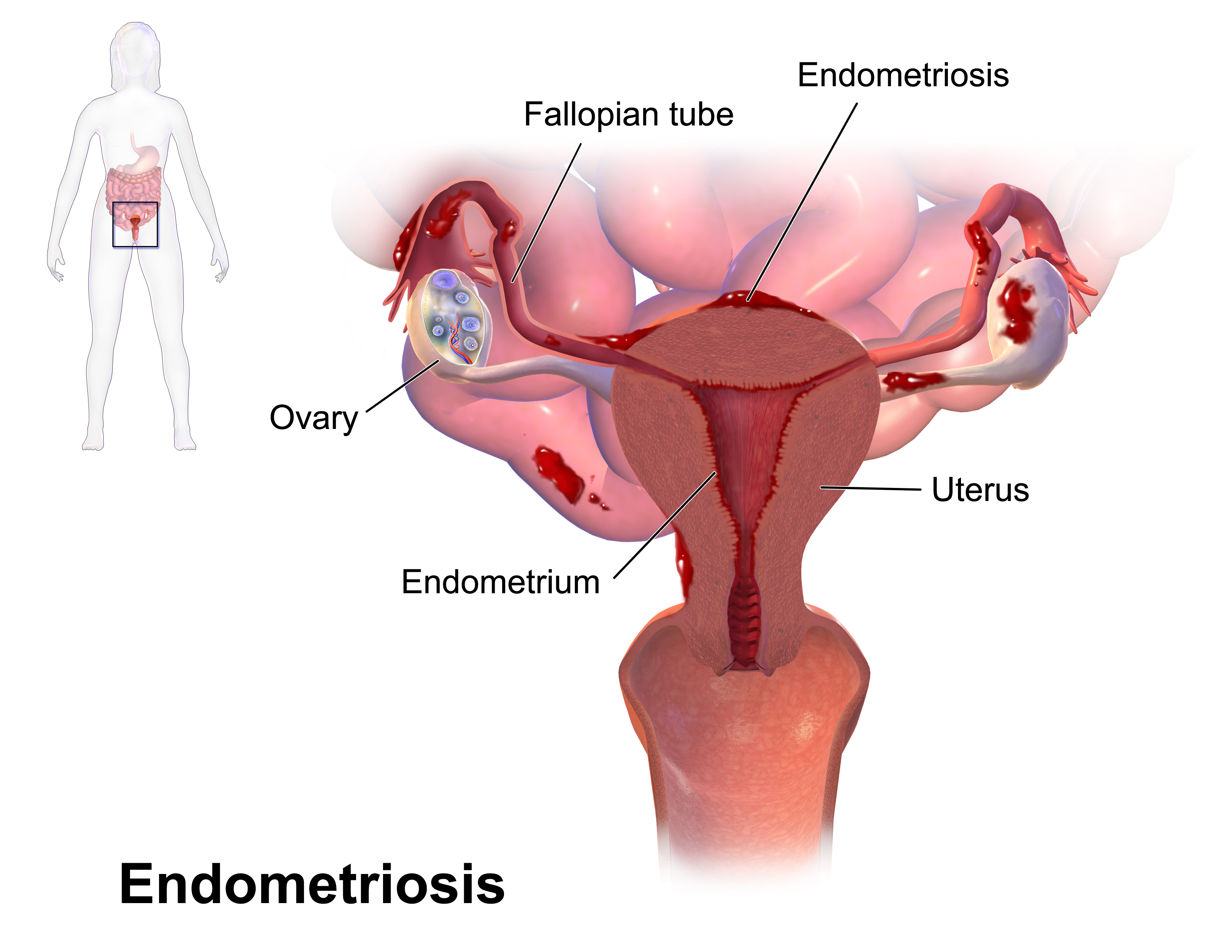
3. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is when the tissue that makes up the uterine lining (the lining of the womb) is present on other organs inside your body. Endometriosis is usually found in the lower abdomen, or pelvis, but can appear anywhere in the body
Other causes of fallopian tube blockage include infections, ruptured appendix, genital tuberculosis, and ectopic pregnancy.
What are the Diagnosis of Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
1.Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
An HSG is a special kind of x-ray used to evaluate female fertility. An outpatient procedure, the test takes no longer than a half hour. It involves placing an iodine-based dye through the cervix and taking x-rays. These x-rays help evaluate the shape of the uterus and whether the fallopian tubes are blocked.
2. Chromotubation
It is a procedure usually done during a laparoscopy to visualize the fallopian tubes in order to see if they are patent or open. It’s done during an infertility work-up. It is a procedure where a colored dye is passed through the fallopian tubes to confirm that they are patent.
3. Sonohysterography
is a special kind of ultrasound exam. Fluid is put into the uterus through the cervix using a thin plastic tube. Sound waves are then used to create images of the lining of the uterus. The fluid helps show more detail than when ultrasound is used alone.
What are the Treatment Options of Fallopian Tubes?
1.Tubal re-anastomosis
Tubal re-anastomosis is also known as a tubal reversal, tube ligation reversal or tube sterilization reversal.
Before the commencement of the procedure, certain tests are done as mentioned above.
General anesthesia is given to the patient.
Then, the doctor places a laparoscope by making a hole below the belly area. The laparoscope is then guided to the pelvic area.
The fallopian tubes are then monitored and accordingly the procedure is commenced.
Any rings or clips in the tube are removed. Then, the ends of the tubes are reconnected with the help of small stitches.
This procedure takes around 2-3 hours. Proper rest is recommended to the patient for the next 3 days at the hospital itself. The doctors monitor the progress in the health of the patient.
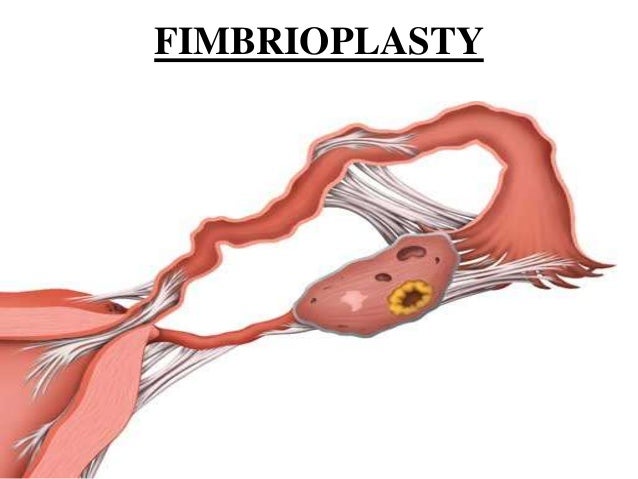
2. Fimbrioplasty
Fimbrioplasty is a procedure where fimbriae are reconstructed along with the removal of damaged or functionless fimbriae. Fimbrae basically are small, finger-like projections present near the ovaries.
This treatment is preferred in women who have low fertility levels due to fimbrae problems.
Moreover, after the successful completion of fimbrioplasty, it is noted that women conceive naturally in a short time.
But you need to know that there are more chances of having an ectopic pregnancy if the pregnancy is achieved after fimbrioplasty.
3. Salpingectomy
This procedure mainly involves the removal of a part of the fallopian tube. It was earlier done with the help of laparotomy. In the recent times, it is done with the help of laparoscopy.
Nowadays, laparoscopic salpingectomies are more commonly utilized as a part of the minimally invasive procedures.
One of the common ways utilized is to use a pre-tied surgical loop. It is used to tighten a knot around the fallopian tube and a part of the tube is removed from its place.
Doctors take care that the surrounding areas and nearby reproductive parts are not affected during the removal of a part of the fallopian tube.
4. Salpingostomy
Salpingostomy is also known as neo salpingostomy. It is a procedure, which is used when the hydrosalpinx (blocked and swollen tube) obstructs the end of one or both the fallopian tubes.
Then, the surgeon makes another opening near the end of the fallopian tube. This opens to the ovary.
This helps in the removal of the blockage and successful occurrence of a pregnancy. The doctor opens the fallopian tube. Then, he removes the blockage. The tube is left intact.
The doctor leaves the incision open as it heals on its own.
He/she advises the patient to take proper precautions to avoid increased chances of infections after the completion of the surgery.
5. Tubal Cannulation
In the procedure of tubal cannulation, the doctor inserts a tube known as a catheter through the vagina of the patient.
Ultrasound is utilised for viewing the fallopian tubes. This helps the doctor to insert the catheter in the right location.
The blocked area in the fallopian tube is opened up with the help of a balloon at the end of the catheter or wire.
It can be done after the completion of the procedure known as hysterosalpingography.
Mild sedative and anaesthesia are given to the patient before the commencement of the tubal cannulation procedure.