Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Your first symptom of gynecomastia can be a lump of fatty tissue under the nipple. Often the lump is tender or sore.
This may make you worry that you have breast cancer, which occurs in a small number of men. Gynecomastia is not usually a symptom of cancer, but your doctor can do some tests to rule it out.
Swelling of the breasts can occur unevenly, with one being larger than the other. You may have breast tenderness, too.
See your doctor if you find that your breasts are swollen, sore, or tender, or that one or both breasts are discharged from the nipple.
Treatment options for gynecomastia Surgery in Bangalore
Gynecomastia normally resolves without any medication, but if there is an underlying disorder, treatment may be required.
If the condition is due to a drug, the patient may need to turn to another drug. If the patient only takes the drug for a short period, the illness may be temporary.
If the condition may not heal within 2 years or causes embarrassment, pain or tenderness, care may be required.
Treatment is very rare. Options include breast reduction surgery or hormonal treatment to block the effects of estrogens.
What are the signs and symptoms of gynecomastia?
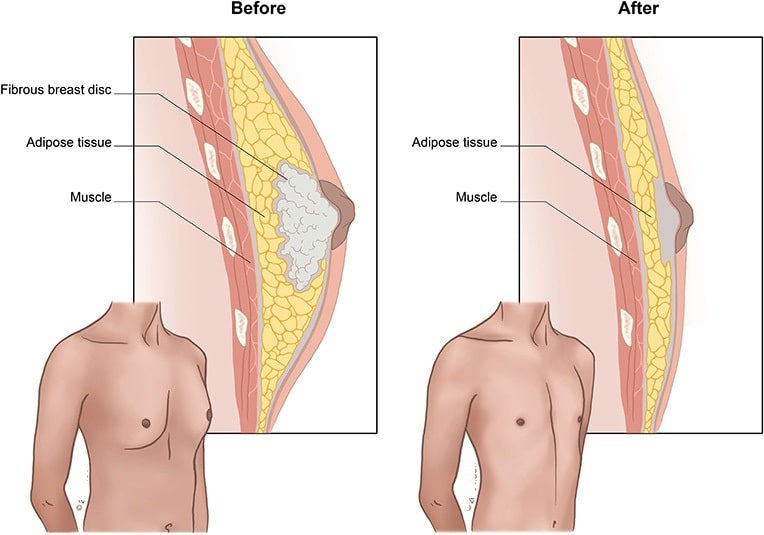
Male breast enlargement is the main symptom of gynecomastia. Gynecomastia, as described earlier, is the enlargement of the glandular tissue rather than the fatty tissue. It is usually symmetrical with respect to the nipple and may have a rubbery or firm feel. Gynecomastia typically occurs on both sides but can be unilateral in some cases. Enlargement can be stronger on the one hand, even though both sides are involved. Tendency and sensitivity can be present, but there is normally no serious pain.
The most significant difference between gynecomastia and male breast cancer is that it accounts for only 1% of the total cases of breast cancer. Typically, cancer is restricted to one limb, is not necessarily focused around the nipple, feels hard or solid, and may be associated with dimpling of the skin.
How do I know if I have gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is characterized as the presence in a male of breast tissue greater than 0.5 cm in diameter. Gynecomastia, as discussed earlier, is the presence of true breast (glandular) tissue, usually found around the nipple. Fat deposition is not believed to be genuine gynecomastia.
Careful medical history, including prescription and drug use, is also relevant. If there is a suspicion of cancer, a mammogram can be requested by a health care provider. Further testing may be recommended to help assess the cause of gynecomastia in some cases.
This may include blood tests to assess the function of the liver, kidney, and thyroid. Measurements of hormone levels in the bloodstream can also be prescribed in certain cases.
Recovery of Gynecomastia Surgery
While pubertal gynecomastia normally decreases on its own, in rare cases it can continue requiring care. It can occasionally remain, which needs care. Gynecomastia that has been present for 12 months or more (long-term) may experience scarring (fibrosis) which makes treatment with drugs far more difficult, if not impossible, to react. Psychological effects may occur if breast enlargement is pronounced or a source of embarrassment.
Can Gynecomastia be prevented?
Gynecomastia that occurs due to hormonal changes in growth or aging cannot be avoided. Gynecomastia linked to medical conditions can be avoided only to the degree that the underlying or liable condition can be prevented.
What is the Gynecomastia Surgery Success rate in Bangalore?
The prevalence of asymptomatic gynecomastia is 60 to 90 percent in girls, 50 to 60 percent in adolescents, and up to 70 percent in men between 50 and 69 years of age. Popular causes of gynecomastia include puberty, excess weight gain, anabolic steroid use in bodybuilders, and marijuana use.