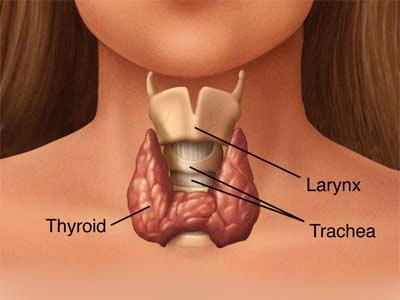
The thyroid is shaped like a little butterfly or bow tie and it sits under the skin in the front of your neck.
It makes two hormones that are secreted into the blood: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).These hormones are necessary for all the cells in your body to work normally.
The thyroid is directly connected to the body’s metabolic system. It also plays a role in reproductive health, fertility and even cardiovascular health. Yet thyroid problems affect people in different ways. The vast number of symptoms and conditions connected to the thyroid are one of the reasons so many myths exist about the thyroid disorders.
What does my thyroid gland do?
The thyroid makes two hormones that it secretes into the blood stream. One is called thyroxine; this hormone contains four atoms of iodine and is often called T4. The other is called triiodothyronine, which contains three atoms of iodine and is often called T3. In the cells and tissues of the body the T4 is converted to T3. It is the T3, derived from T4 or secreted as T3 from the thyroid gland, which is biologically active and influences the activity of all the cells and tissues of your body
What do my thyroid hormones do for me?
The T4, or rather the T3 derived from it, and the T3 secreted directly by the thyroid gland influence the metabolism of your body cells. In other words, it regulates the speed with which your body cells work. If too much of the thyroid hormones are secreted, the body cells work faster than normal, and you have hyperthyroidism. If you become hyperthyroid because of too much secretion of the hormones from the thyroid gland, the increased activity of your body cells or body organs may lead, for example, to a quickening of your heart rate or increased activity of your intestine so that you have frequent bowel motions or even diarrhoea.
On the other hand if too little of the thyroid hormones are produced (known as hypothyroidism), the cells and organs of your body slow down. If you become hypothyroid, your heart rate, for example, may be slower than normal and your intestines work sluggishly, so you become constipated.
What can go wrong with my thyroid?
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) – not enough thyroxine is produced for the body’s needs.
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) – too much thyroxine is produced for the body’s needs.
- Hypothyroidism is the most common disorder.
Symptoms:
Hypothyroidism: tiredness, feeling cold, weight gain, poor concentration, depression.
Hyperthyroidism: weight loss, heat intolerance, anxiety, and, sometimes, sore and gritty eyes.
What other disorders are there?
- Thyroid eye disease – this affects some people who have an overactive thyroid due to Graves’ disease.
- Nodules or swellings – these lumps can stop the thyroid gland from working properly, or are simply uncomfortable.
- Thyroid cancer – this is very rare, but it is important to ask your doctor to check any lump in your neck.
What causes a thyroid disorder?
There are many different causes of the different thyroid disorders. Most commonly the cause is due to autoimmune thyroid disease – a self-destructive process in which the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid cells as though they were foreign cells. In response the thyroid gland becomes under active (hypothyroidism) or overactive (hyperthyroidism). You may find that other members of your family have thyroid problems or another autoimmune disorder.
How to Diagnose?
However, by taking a small sample of your blood he or she can assess exactly your thyroid secretory state. On this single sample of blood, for example, the levels of the hormones involved can be measured in the laboratory. By this means it is possible to find out if too much or too little T4 and/or T3 is being secreted, and how active the pituitary is by measuring the TSH. A single blood test will normally confirm the diagnosis, but sometimes other tests are required.
How is my thyroid gland controlled?
There has to be some sort of mechanism that regulates very carefully the amount of T4 and T3 secreted by your thyroid gland so that the right – the normal – amounts are manufactured and delivered into the blood stream. The mechanism is very similar to that which regulates the central heating in a house where there is a thermostat in, say, the living room, which is set to a particular temperature and which activates the gas- or oil-fired furnace, or boiler that heats the hot water. In the case of the thyroid the ‘thermostat’ consists of a little gland, called the pituitary gland that lies underneath your brain in your skull. The pituitary senses the level of thyroid hormones in your blood stream, just as the thermostat in your living room senses the temperature. Under normal circumstances, if the level drops just a little below normal, the pituitary reacts by secreting a hormone called the thyroid stimulating hormone, also known as TSH, and this hormone activates the thyroid gland to put out more T4 and T3.
Conversely, when the thyroid hormone levels rise above normal the ‘thermostat’ senses this and the pituitary stops secreting TSH so that the thyroid gland stops working so hard and the secretion of T4 and T3 is reduced.
Treatment:
Hyperthyroidism Treatment:
Thyroid hormone production can be slowed or stopped completely with:
Radioactive iodide treatment
Anti-thyroid medication
Surgery
Hypothyroidism Treatment:
Someone with hypothyroidism will have to take thyroid hormone replacement for the rest of his/her life. No surgery, drugs, or complementary medicine can boost your thyroid once it slows down.
Diet and Nutrition:
Protein, calcium, magnesium, and iodine help your thyroid work. Make sure you’re getting plenty of all the B vitamins, vitamin A, and vitamin C intake.